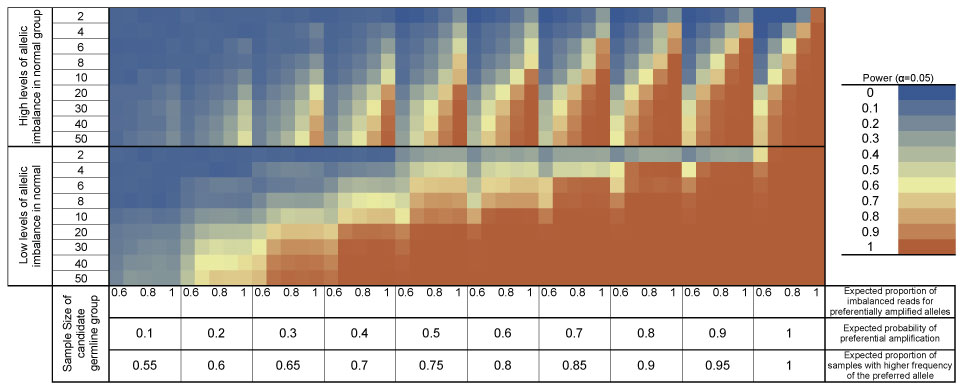
The Somatic-Germline Interaction (SGI) tool is a software package designed to identify statistical interaction between germline variants and somatic mutational events from next-generation sequence data. SGI interfaces with VAAST to identify candidate germline susceptibility variants from case-control sequencing data. SGI then analyzes tumor-normal pair next-generation sequence data to evaluate evidence for somatic-germline interaction in each gene or pathway using two tests: the Allelic Imbalance Rank Sum (AIRS) test and the SomaticMutation Interaction Test (SMIT). AIRS tests for preferential allelic imbalance to evaluate whether somatic mutational events tend to amplify candidate germline variants. SMIT evaluates whether somatic point mutations and small indels occur more or less frequently than expected in the presence of candidate germline variants. The SGI test combines AIRS and SMIT to provide a single, unified measure of statistical interaction between somatic mutational events and germline variation. SGI can be used to increase the power of rare variant association studies in cancer and to validate the potential causative role of germline cancer-susceptibility variants.
Licensing and Download
Software implementing the SGI algorithm is now available for academic, non-commercial use, under the SGI Academic License Agreement. Register to download the most recent version here.
Presentation
The slides from the SGI presentation at PSB 2014 are available for download: SGI Presentation
